Scientists Propose New Nanocomposites for EMI Shielding Materials
Date:07-04-2020 | 【Print】 【close】
The forthcoming telecommunication system and electronic interfaces acquires a wide frequency range, which causes a series of electromagnetic (EM) pollution to the humankind.
So, it’s important to establish a frontline technological platform to create an ideal nanomaterial and its nanocomposite for efficient attenuation of EM and radiation interferences (EMI) pollution.
A research team led by Prof. ZHU Pengli and her post-doctoral researcher Dr. Krishnamoorthy Rajavel from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently established a multifunctional property of 2D MXene filled polymer nanocomposites for EMI shielding materials with excellent heat dissipation.
The successful introduction of chemically exfoliated stacked bulk MXene (Ti3C2Tx) into polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) polymer matrix appreciably increased EMI shielding performance along with remarkable thermal conductivity.
The change in the local field due to the heterogeneous combination of a polymer matrix and electrically conducting filler materials (MXene) possessed the absorption dominated mechanism in attenuation of incoming electromagnetic waves.
And also, the combined synergistic effect of electrical network formation and thermal dissipation capability majorly contributed to its enhanced EMI shielding performance.
In general, the proposed combination of stacked MXene filled polymer nanocomposites film possessed several merits such as high dielectric loss, superior electrical and thermal conductivity along with high attenuation of EM pollution which is a requirement for future EMI shielding materials, and could be used in future electronic packaging applications.
The study was published in Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing.
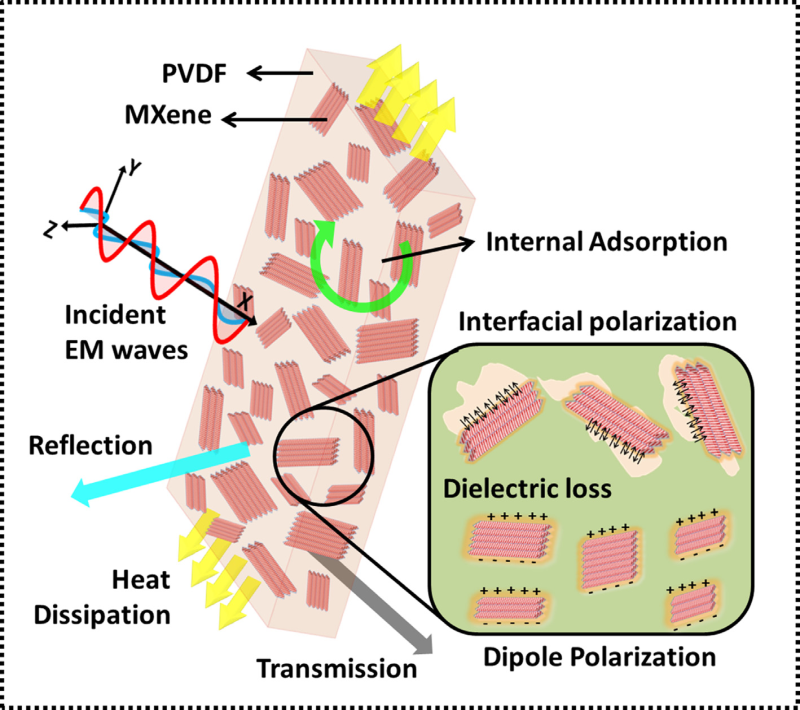
Figure. SEM and TEM images of 2D MXene (Ti3C2Tx), Illustrated EMI shielding mechanism proposed for MXene-PVDF nanocomposites film, thermal conductivity of pure PVDF and MXene-PVDF nanocomposites with various filler loading (0-22.55 vol%), and total EMI SE as a function of frequency for the fabricated PVDF nanocomposites at different MXene loading from 0-22.55 vol%. (Image by Dr. Krishnamoorthy Rajavel)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email: xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn