Researchers Propose Novel Photoacoustic Probe for Early Screening of Prostate Cancer
Date:18-05-2020 | 【Print】 【close】
Photoacoustic imaging (PAI), based on the photoacoustic effect, is a noninvasive imaging modality which has several merits for imaging biological tissues, especially small blood vessels due to high optical contrast of hemoglobin.
Since visualizing new blood vessels is an important indicator of early-stage prostate cancer, PAI promises to be an optimal candidate for prostate cancer diagnosis
Thus, energy-efficient light delivery and good alignment of laser excitation and acoustic detection are very important for optimal imaging sensitivity.
Researchers from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences designed a novel handheld low-cost PAI probe with better performance. The study was published in IEEE Sensors Journal.
The proposed probe was designed in which the light was guided to the sample surface directly below the ultrasound transducer. With this design, the laser energy was utilized with higher efficiency, hence leading to high signal to noise ratio (SNR) and deep imaging penetration.
By using a single optical fiber rather than fiber bundle, the probe was physically compacted, making it user-friendly and clinical applicability.
The sensitivity of the probe was high due to the higher transmission efficiency of the single optical fiber as well as the optimal optical illumination design.
Moreover, the research team collaborated with The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, to execute in vivo animal (healthy Beagle dog) and ex vivo human canine prostate experiments. The results showed that the proposed probe could achieve high light transmission and illumination efficiency, high SNR, large imaging depth, and wide field-of-view (FOV) with laser energy well below the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) safety limit.
This study could potentially improved the quality of life of the suspected prostate cancer patients and also provides better diagnosis at the early stage of the cancer.
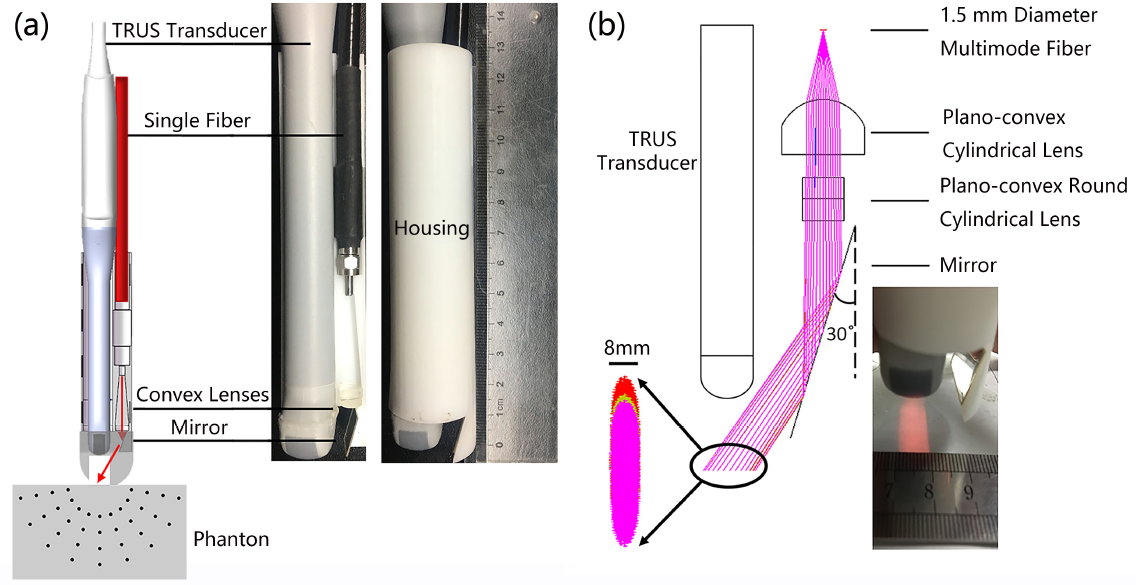
Single fiber-based transrectal PAUS probe design (Image by SIAT)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email: xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn