Researchers Analyze Bioinspired Materials in Terms of Functional and Mechanical Aspects
Date:06-07-2020 | 【Print】 【close】
Biological materials are highly efficient, sustainable, and multi-functional, since they could generate superior properties that fulfill not only mechanical but also various functional needs, although they use limited, weak constituents, e.g., soft proteins and brittle minerals.
One key to achieve this lies in their hierarchical structure, which means that the material has structural elements that organize in multiple levels and different length scales. This provides resourceful inspiration for developing novel materials that are not dependent on complicated chemicals and meanwhile are durable, reliable, and nontoxic.
The hierarchical structure endows interesting functions that are also important to many engineering applications, such as superwettability for directional liquid transport. This structure also leads to exceptional mechanical performance per unit mass, which means they are usually lightweight with high strength and toughness.
Bioinspired materials based on the structure-property mechanisms of biological materials have been the exciting frontier of materials research.
According to a recent publication in Bioactive Materials, Dr. WANG Bin and her colleagues formulated key strategies for bioinspired materials and addressed bioinspired materials from a vast number of fascinating biological materials in terms of functional and structural categories, thus providing a compact overview of the grand panorama of this field.
So far, the development of bioinspired materials includes uncovering the design principles from nature through theorizing fundamental mechanisms, correlating this fundamental understanding to engineering needs/problems, and fabricating hierarchically structured materials through developing fabrication techniques accordingly.
Through paradigmatic biological and bioinspired materials, Dr. WANG and colleagues detailed the representative, impactful types of functions (superwettability, bioactivity, and stimuli-responsiveness) and mechanical properties (light-weight and strong, and light-weight and tough).
Besides the fundamentals for each specific property, they also illustrated the structure-property mechanisms from biological materials to bioinspired materials, and the corresponding development routes targeting exceptional functions/properties for relevant applications.
“Despite current challenges, biological and bioinspired materials have a bright prospect in promoting innovations and breakthroughs in the modern materials industry,” said Dr. WANG.
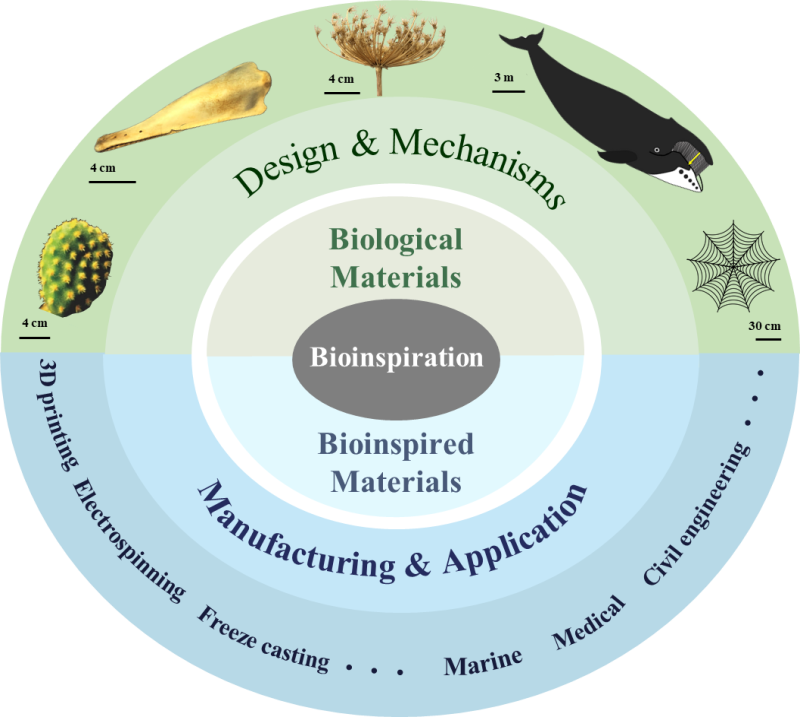
Figure. The development of bioinspired materials from biological prototypes. (Image by Dr. WANG)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email: xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn