Scientists Design and Produce an Injectable Thermo-sensitive Adhesive Hydrogel as Bioactive Wound Dressing
Date:06-08-2020 | 【Print】 【close】
As the largest organ of human body, skin provides a barrier outside the body. Once the skin suffers traumatic or surgical injury, the wound will destroy the barrier function and threaten people's life.
Researchers from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed an injectable thermo-sensitive adhesive hydrogel with the ability of filling irregular defect, tissue adhesiveness, antibacterial and angiogenesis.
This study was punished in Carbohydrate Polymers.
This hydrogel was prepared by incorporation of catechol modified quaternized chitosan (QCS-C) into poly(d,l-lactide)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(d,l-lactide) (PLEL) hydrogel, and loaded with nano-scaled bioactive glass.
The hydrogel presented the transition from a flowing liquid to a solid gel at 32.6 °C, which was quite suitable for fulfilling the complex wounds through injection. Then, this hydrogel showed enhanced adhesive strength after gelation, which could effectively bind the ruptured skin of mice.
Furthermore, the hydrogel showed anti-bacterial activity and exhibited significantly high killing ratio (> 95%) for both Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, which means it possessed biocompatible and biodegradable performance.
The results of mice partial laceration experiments showed that the hydrogel could effectively seal the ruptured skin and significantly accelerate wound healing. Besides, the mechanism of accelerating wound healing could be due to the nano-scale bioactive glass, which would stimulate endothelial cells migration and angiogenesis.
Researchers believes that this investigation of hydrogel wound dressing established a new type of clinical treatment technology for complicated wounds, which is highly needed for complex wounds in clinical treatment.
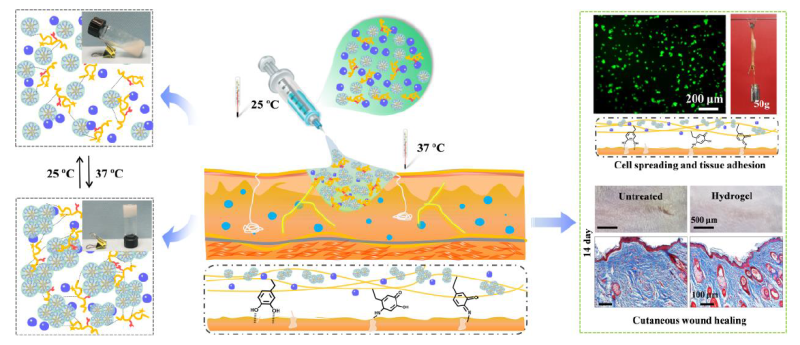
Schematic diagram of thermo-sensitive injectable PLEL-nBG-QCS-C composite hydrogel for wound healing (Image by Dr. ZHAO Xiaoli)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email: xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn