Researchers Induced an Intracellular Polymerization Based Precision Medicine for Cancer Treatment
Date:28-02-2022 | 【Print】 【close】
Cancer is a malignant disease that causes abnormally high death rate. To date, few effective cancer treatment methods have been applied for patients with limited successful examples reported. For late-staged cancers, chemotherapy is one of the most efficient method to prolong patients’ survival periods. To break through the toxicity and specificity limitations of many commercial anticancer drugs, development of new targeted cancer therapeutics is urgently required in the armoury against cancers.
The team from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have explored the possibility of constructing artificial polymers in living cells and found that intracellular polymerization can significantly change the cell cycle, cytoskeleton structure, and cell motility previously (Nature Chemistry, 2019, 11, 578).
On the basis of this study, the authors' team further developed a new method of precision treatment of tumours based on a light induced intracellular control polymerization.
Their study was published in the journal of J. Am. Chem. Soc. Au, on 23 Feb, 2022.
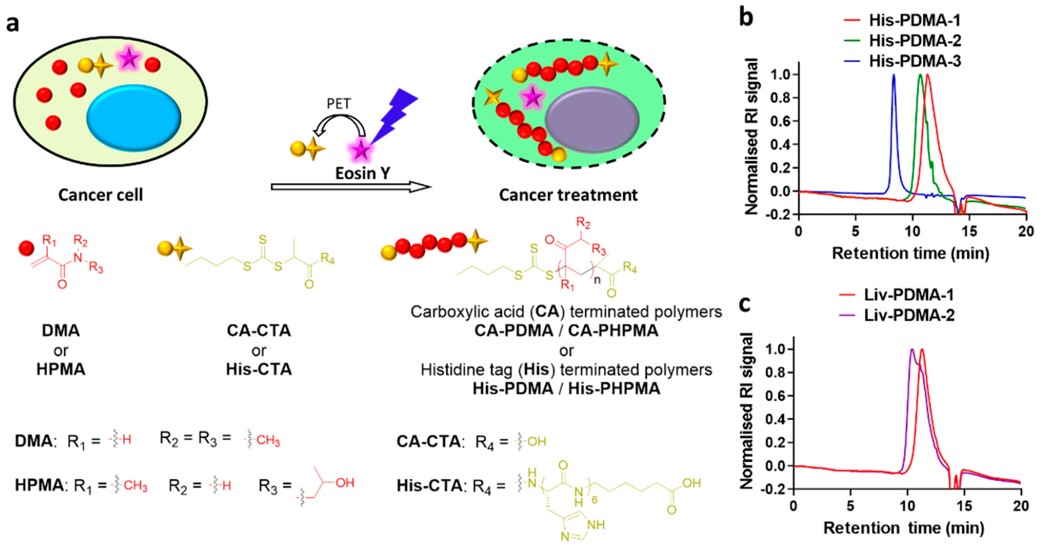
The authors used the method of light-controlled photoinduced electron transfer–reversible addition–fragmentation chain-transfer (PET-RAFT) polymerization instead of free radical polymerization to achieve the development of polymer synthesis methods with predictable and controllable molecular weight, and at the same time greatly reduced the molecular weight distribution of the obtained polymers, effectively improve the regularity of the polymer and the controllability and reproducibility of the intracellular polymerization system.
At the same time, the team further explored the application potential of the intracellular polymerization system, screened a library of monomers for the purpose of tumor treatment, and successfully developed a precision tumor treatment system based on intracellular polymerization. Through the screening of cytotoxicity, the team found that a class of acrylamide polymer monomers with low toxicity can significantly improve their cytotoxicity after polymerization, efficiently induced apoptosis and necrosis in tumor cells, where they have developed a new precision tumor treatment method.
Finally, the research team verified the biosecurity of the intracellular polymerization prodrug system, and found that the body weight, hematological parameters and histological characteristics of the main organs of the experimental animals were not affected by intracellular polymerization or arbitrary component administration, which fully verified the biosecurity of the system.
"We believe that the precision tumor treatment method based on intracellular polymerization developed by this work will open a new era in polymer therapy for cancer treatment," said GENG Jin, the leader of this study.
Intracellular PET–RAFT polymerization. (Image by SIAT)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email:xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn