Researchers Unveil the Diversity and Impact of Broad Host Range Plasmids in the Human Gut
Date:26-06-2023 | 【Print】 【close】
The human gut hosts a complex ecosystem comprising an intricate plasmidome with abundant undiscovered plasmids, driving horizontal gene transfer events. Broad host range (BHR) plasmids carrying fitness genes transfer between bacteria across distantly phylogenetic taxa, facilitating the adaptation of their hosts to varying environments. However, accurate identification of BHR plasmids in the gut is still difficult. Moreover, their host range and prevalence remain unclear.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. MA Yingfei from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has identified and characterized the plasmids harbored by the human gut bacterial isolates from culturomics-based studies. The researchers have revealed their accurate host range, persistence in the human gut, accessory genes, prevalence across various environments, and transmission and evolutionary trajectories in detail.
This study was published in Nucleic Acids Research on Jun. 8.
Researchers assembled 820 plasmid-like clusters (PLCs) with high-completeness genomes (comPLCs). "We found that the majority of PLCs (81.1%) were classified to known replicon types which suggested gut plasmids were highly diverse and novel," said YANG Lili, the first author of this research.
Researchers revealed 175 comPLCs had a broad host range across distinct bacterial genera, of which, 71 were detected in at least two human populations from 4 distant countries, and 13 were highly prevalent (>10%) in at least one human population. "We observed that the broadest PLC (Clstr-417) could spread among the isolates collected from Chinese donors and American donors of 24 genera across 5 phyla. And some PLCs are so ubiquitous that can even be detected in different species and environmental sewage," added YANG Lili.
The evolutionary trajectory showed that the BHR plasmid spread between the phyla and the environment was extremely rapid, with all transmission times occurring 0-10 years ago and colonizing the individual gut multiple times. "We found that these BHR plasmids could carry many different adaptive genes, and individual PLCs even could carry up to seven antibiotic resistance genes. We are concerned about the potential implications of the globally-transmitted plasmids for human health. "said Prof. MA.
Prof. MA is considering more possibilities for BHR plasmids. "BHR plasmids may also have great potential to edit the genome of commensal gut microbes and bacteriophages that suffer from lacking editing tools." Prof. MA said.
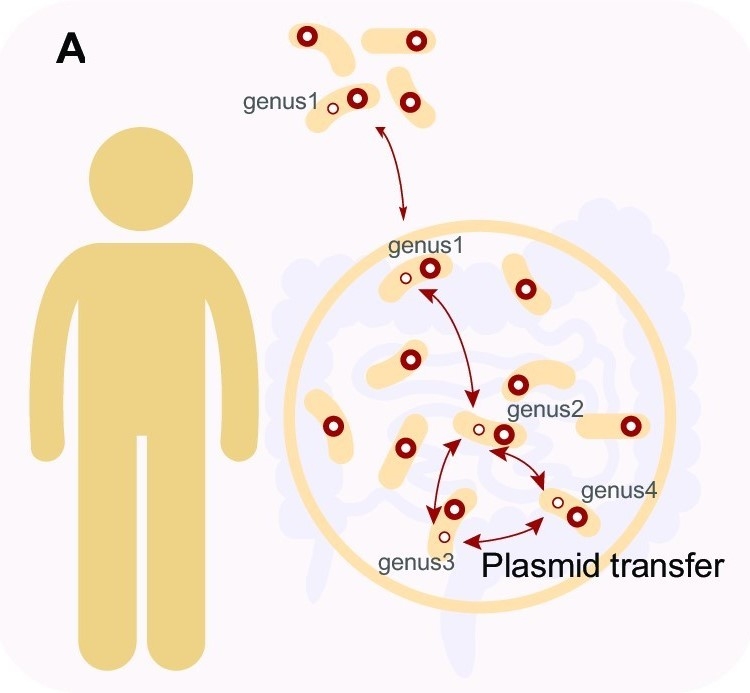
Fig.1 Transfer of BHR plasmids between phylogenetically different hosts in and out of the human gut. (Image by SIAT)
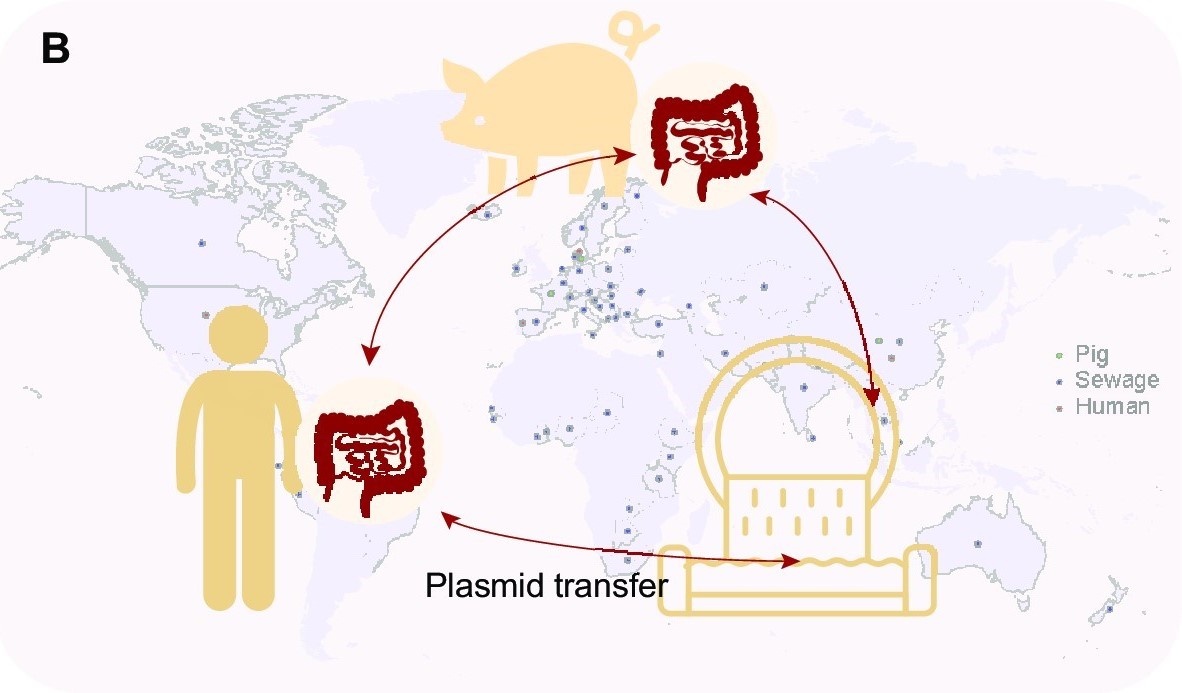
Fig.2 Transfer of BHR plasmids between different populations and environment niches in global. (Image by SIAT)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email:xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn