Can Monkeys Read Emotions From Human Faces?
Date:12-09-2023 | 【Print】 【close】
Being able to read others’ affective states and intentions from facial expressions is crucial for social interaction. Nonhuman primates share the same ability as humans to express emotions via facial expressions, yet we are not sure whether monkeys can read emotions from the faces of other species (e.g. humans). One plausible reason is that we rarely think of investigating emotional perception from the perspective of monkeys.
Recently, a research group led by Dr. DAI Ji from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) systematically investigated how monkeys perceive emotions from human faces and monkey faces with eye-tracking technology and sophisticated behavioral tasks, namely the temporal discrimination task (TDT) and the face scan task (FST).
The study was published in Zoological Research on Aug. 4.
In the first experiment using TDT, monkeys were trained to determine the presenting duration (longer or shorter than 1 second) of human and monkey faces, which included three different expressions (positive, negative, neutral). From this behavioral paradigm, a subjective time perception curve could be built for each monkey. Researchers found that monkeys showed prolonged subjective time perception in response to negative facial expressions in monkeys. In the meantime, pupil tracking revealed that monkey faces also reliably induced divergent pupil contraction in response to different expressions, while human faces and scrambled monkey faces did not.
In the second experiment using FST, monkeys were trained to observe monkey and human faces freely. This experiment intended to uncover monkeys’ scanning patterns on human or monkey faces. The results indicated that monkeys only displayed bias towards emotional expressions upon observing monkey faces. In addition, masking the eye region marginally decreased the viewing duration for monkey faces but not for human faces.
Overall, this study demonstrates that monkeys are more sensitive to facial expressions of conspecifics than those of humans, thus arguing the suitability of using human faces as visual stimuli in monkey studies targeting emotion-related problems.
"This unique experimental paradigm used in the current study sheds new light on inter-species communication through facial expressions between nonhuman primates and humans," said Dr. DAI.
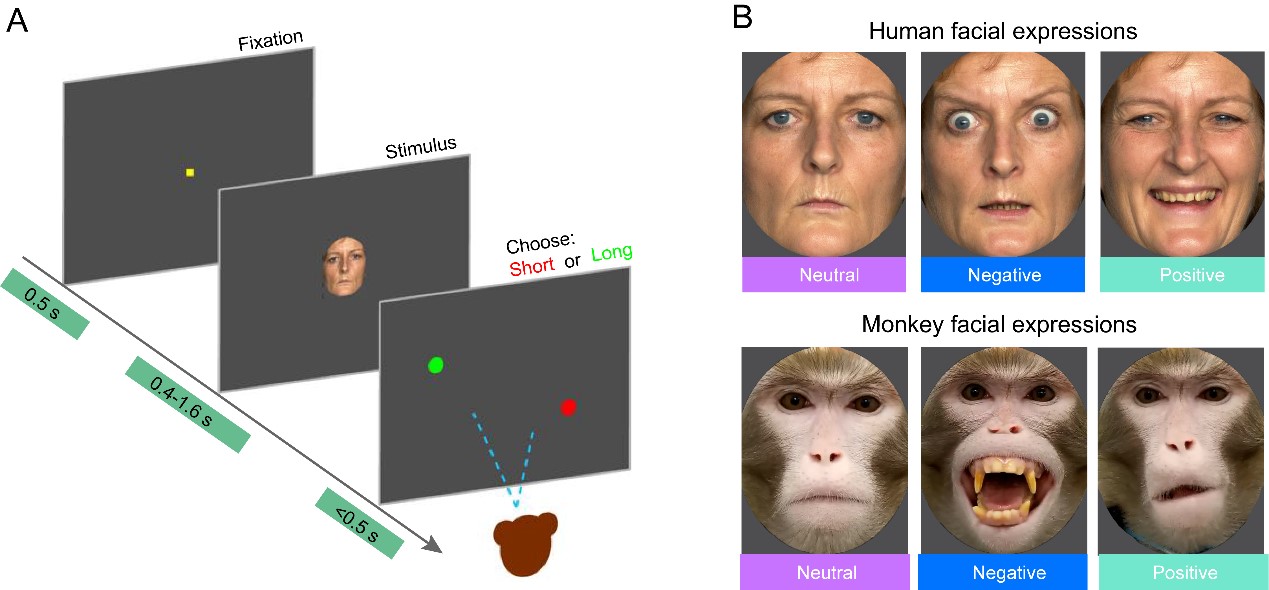
Fig. 1 (A) The schematic of the temporal discrimination task (TDT). (B) Examples of human facial expressions and monkey facial expressions used in the TDT task. (Image by SIAT)
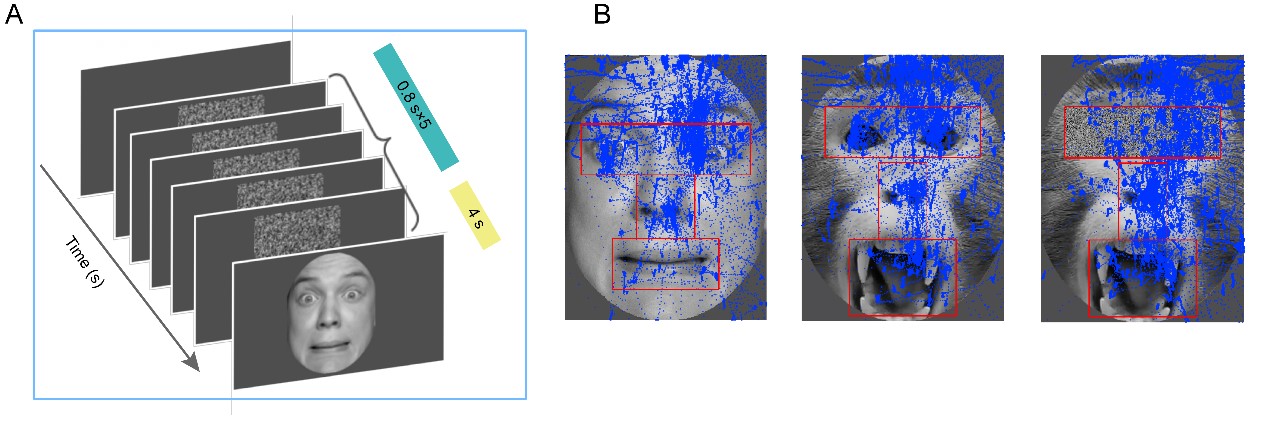
Fig. 2 (A) The schematic of the FST. (B) Examples of facial stimuli and the definitions of eye, nose, and mouth regions (marked in red) for a human face, a monkey face, and a monkey face with scrambled eyes. (Image by SIAT)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email:xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn