Active-Navigation, Stiffness-Tunable Microrobots for Precise Biopsy and Targeted Delivery in Narrow Luminal Interventions
Surgical tasks in small tortuous lumens demand interventional instruments with controllable mechanical adaptability. However, current microcatheters lack a non-disruptive, integration-ready strategy for dynamic stiffness tuning—critical for meeting the divergent mechanical demands for compliant steering and stable advancement.
In a study published in Nature Communications, a research team led by Prof. XU Haifeng at the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed a microrobotic system based on a helix-shaped magnetic soft microrobot, the Helixoft.
The system can be seamlessly integrated into commercial microcatheters, enabling continuous stiffness tuning spanning up to a 40-fold range and precise active steering with bending angles of up to 118°, both functions are achieved solely through magnetic control and without reliance on potentially harmful external stimuli.
The present Helixoft system is specifically designed for navigation within narrow and sensitive luminal environments by miniaturising the variable-stiffness catheter to a diameter of 300 μm. Achieving tunable mechanical performance at the microscale remains a major challenge, as miniaturisation inherently conflicts with the complex structural requirements for stiffness tuning. This microrobotic system addresses this challenge based on a previously underutilised mechanism that harnesses microscale helical motion at the component level to dynamically modulate the otherwise static mechanical properties of the overall structure under a magnetic field. Through a decoupled magnetic control strategy, independent remote tuning of stiffness and active steering is achieved by combining helical motion with torque-driven bending of individual microrobotic components. This mechanism eliminates the need for potentially harmful stimuli such as thermal, optical, or electrical inputs.
In addition, the Helixoft microcatheter exhibits strong functional extensibility, enabling independently controlled, multi-segment stiffness tuning and seamless integration of auxiliary microsurgical tools—including mini-cameras, electrodes, and laser fibres—for real-time imaging, tissue ablation, and multimodal minimally invasive procedures. Furthermore, repeated in vivo validations across different animal models, together with systematic safety evaluations, confirm both the feasibility and biocompatibility of the Helixoft system.
The Helixoft system provides a minimally disruptive robotic strategy for the mechanical reconfiguration in confined and sensitive luminal environments.
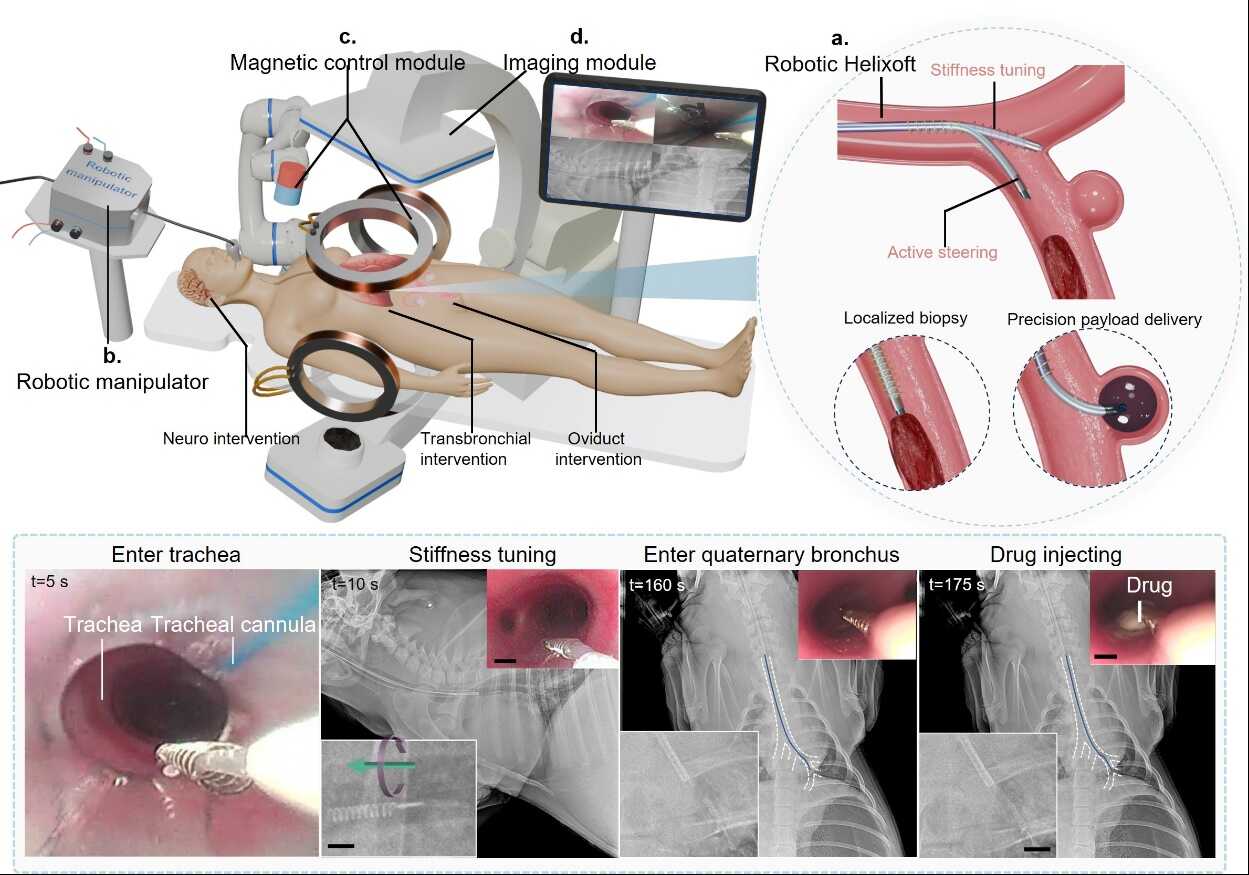
Helixoft microrobotic system for stiffness tuning and active steering of microcatheters during interventional surgeries. (Image by SIAT)
File Download: