SIAT Research
-
Mar 15, 2022Live Fast, Die Young? or Live Cold, Die Old?Based on these results, body temperature seems to be a much more important mediator of lifespan than metabolic rate. For this reason, maybe we should change the saying from "live fast, die young" t... Researchers from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with collaborators from Wenzhou University and the University of Aberdeen, have found...
-
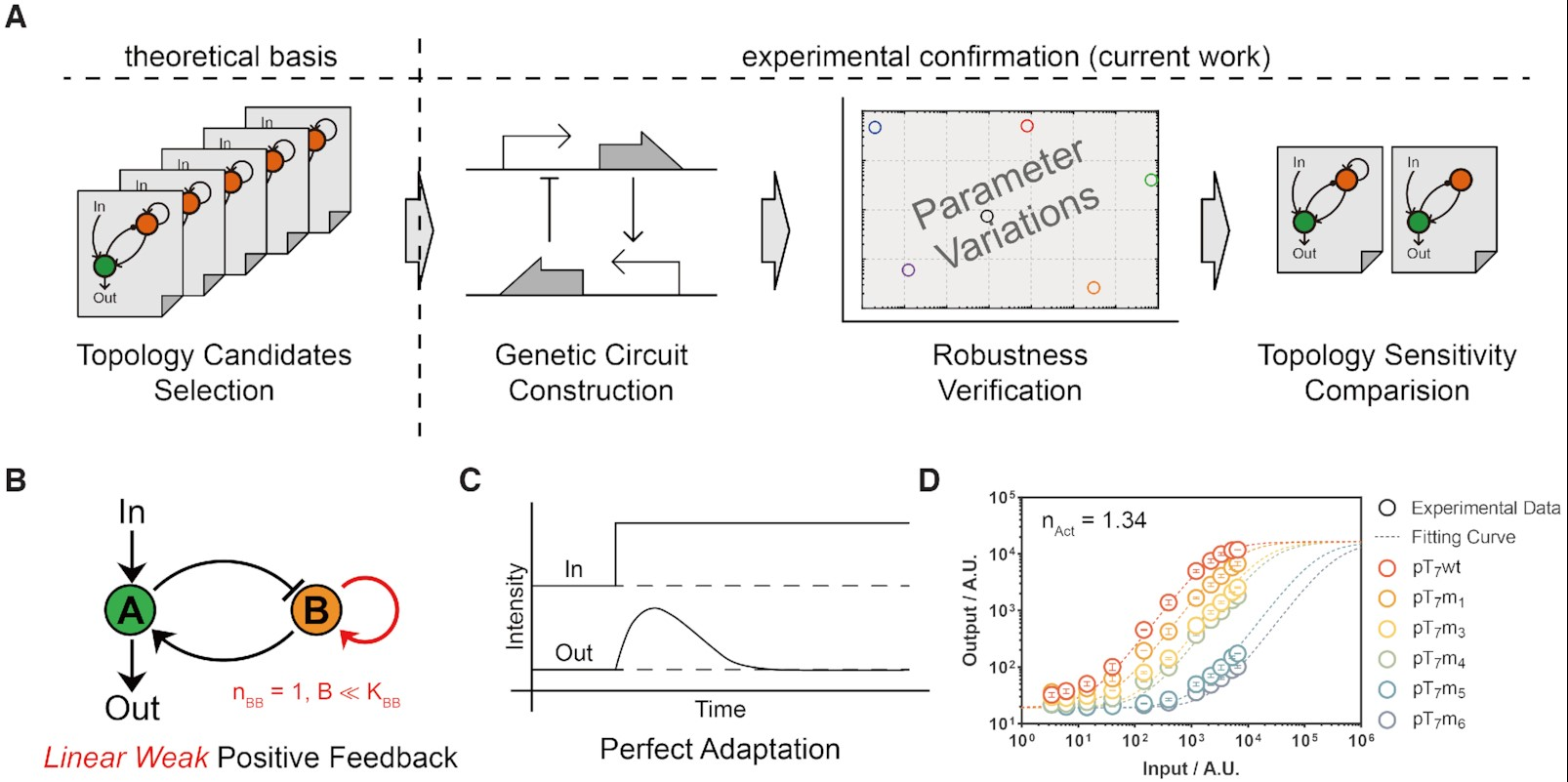
Mar 04, 2022Researcher Develop New Synthetic Genetic Circuits for Prefect Adaptation FunctionThis study addresses the serious problems of poor stability, functional fragility and susceptibility to interference of synthetic genetic circuits in synthetic biology, and proposes the principle o... Since the sophisticated genetic circuits can be very subtle, external environmental variability and host evolutionary instability have emerged as key factors impeding the predictable design of gene...
-
Mar 03, 2022Women Are More Susceptible to Alzheimer's disease: New EvidenceMoving forword, the team is extending this theory to numerous age-dependent chronic diseases such as diabetes, atherosclerosis, cancer, and aging. Epidemiological studies have shown that women are twice as likely as men to develop Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but the cause of this phenomenon has been unclear.Now, however, a study led by Prof. Y...
-
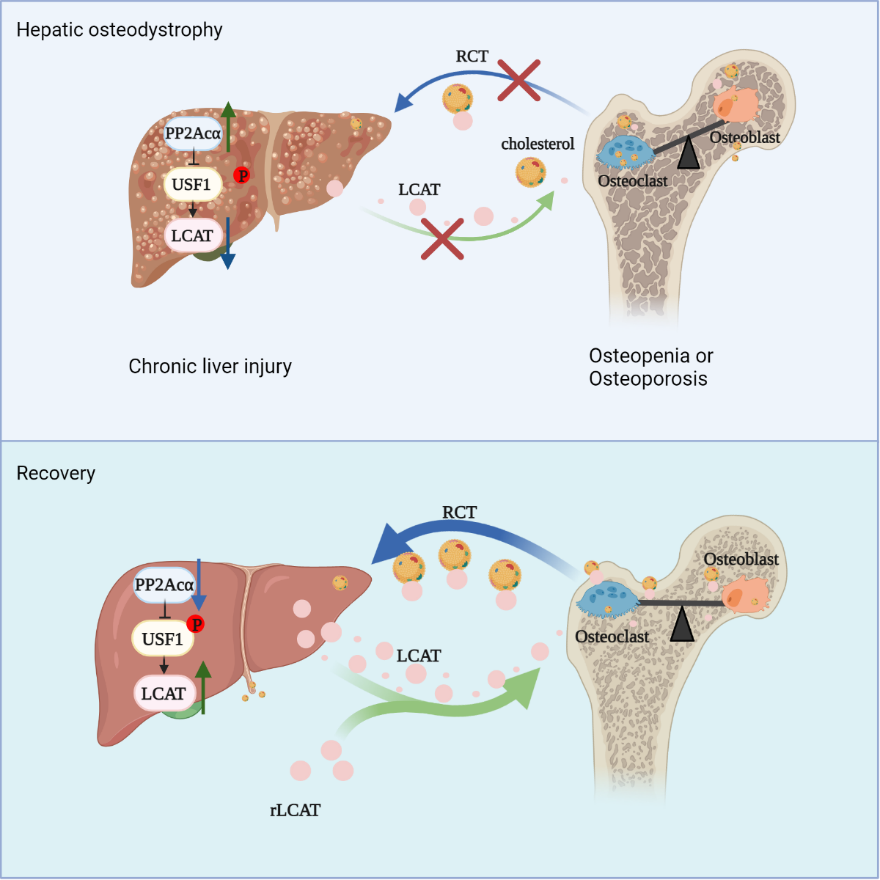
Mar 02, 2022Scientists Reveal How Chronic Liver Injury Causes Bone LossThe study was published in Cell Metabolism on March 1. A research team led by Prof. CHEN Di from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences along with other collaborators have revealed the molecular mechanis...
-
Feb 28, 2022Researchers Induced an Intracellular Polymerization Based Precision Medicine for Cancer Treatment"We believe that the precision tumor treatment method based on intracellular polymerization developed by this work will open a new era in polymer therapy for cancer treatment" Cancer is a malignant disease that causes abnormally high death rate. To date, few effective cancer treatment methods have been applied for patients with limited successful examples reported. For l...
-
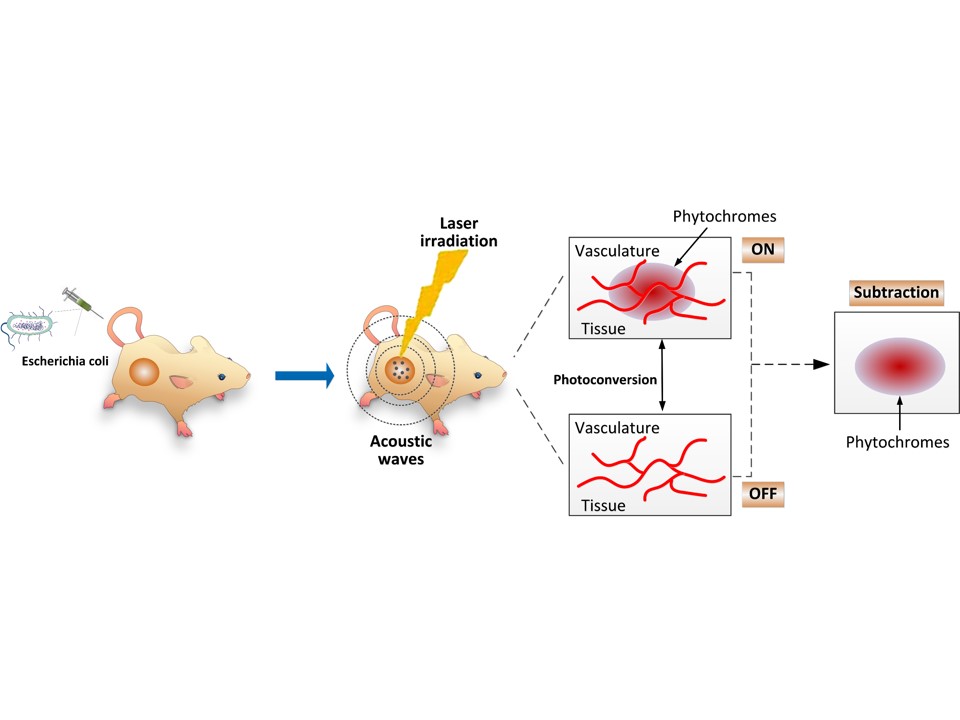
Feb 23, 2022New Approach Enables Background-suppressed Tumor-targeted Photoacoustic ImagingIn this study, the researchers proposed an approach called GPS localization. In this approach, “G” stands for genetically encoded probe, “P” for photoacoustic imaging, and “S” for synthetic b... A research team led by Prof. LIU Chengbo, Prof. YAN Fei, and Prof. CHU Jun from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. ...
-
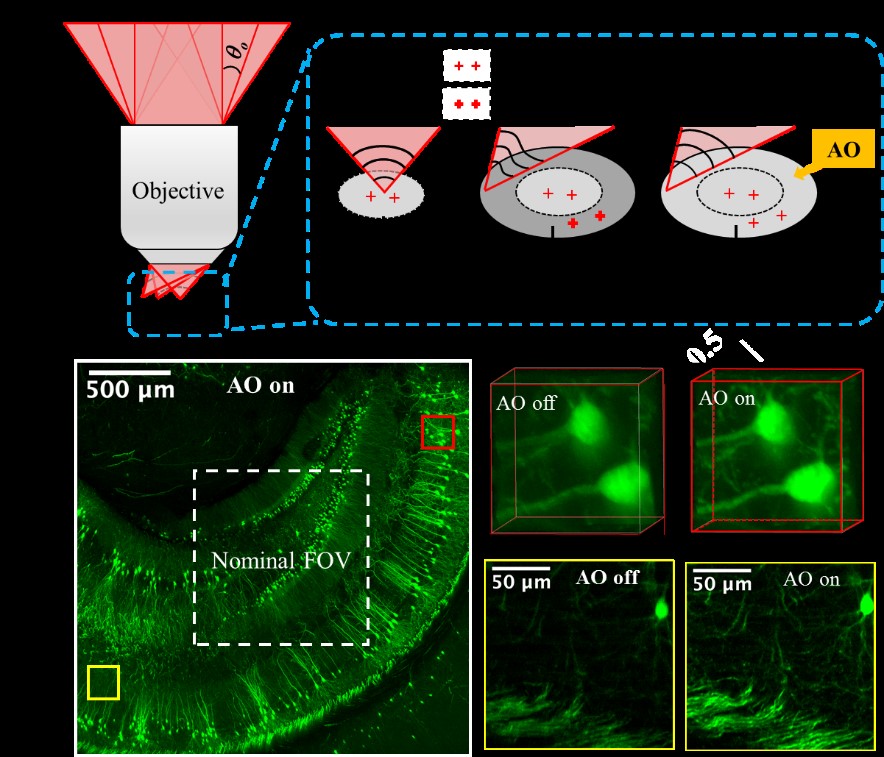
Feb 22, 2022Researchers Develop Large-FOV and High-Resolution Two-Photon MicroscopeThe team proposed a simple and effective method to extend the FOV of a commercial objective using adaptive optics. Two-photon microscopy (TPM) enables the observation of cellular and subcellular dynamics and functions in deep nervous tissues, providing critical in situ and in vivo information for understanding ...
-
Feb 21, 2022Researchers Develop New NFT-Based Framework for Tokenizing PatentsThe team proposed a layered conceptual NFT-based patent framework capable of guiding for businesses in taking advantage of NFTs in real-world problems such as grant patents, funding, biotechnology,... By taking advantage of blockchain technology, digital assets are broadly grouped into fungible and non-fungible tokens (NFT). NFT has widely attracted attention, and its protocols, standards, and a...